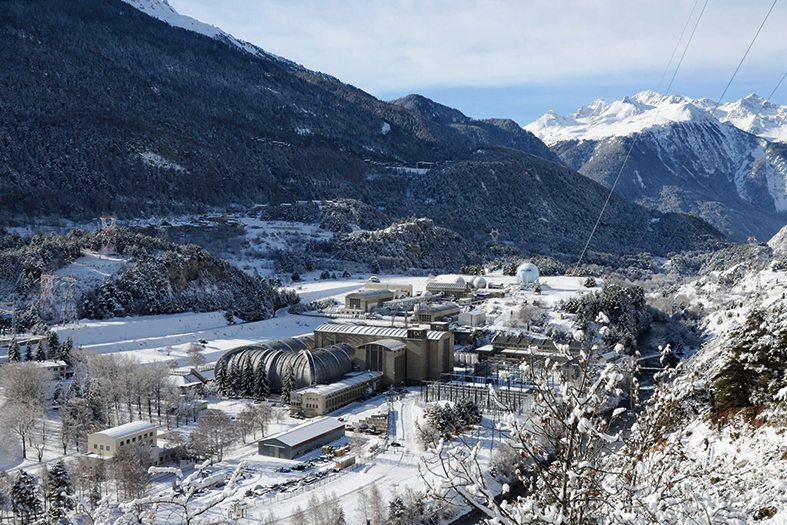
Well before the Wright brothers took the flight that changed the world, wind tunnels were already at the cutting edge of aviation. From the safety of the ground, facilities like ONERA’s have helped aviation pioneers evaluate how new designs will perform in flight. Ever since ONERA’s foundation in post-war Europe, their 12 tunnels have tested the aerodynamics on important new planes from Europe and beyond, including Concorde, the Airbus A380, and the Eurofighter.
ONERA has 12 tunnels at three different sites, to cover all manner of test requirements. They have hypersonic tunnels for aerodynamics, low-speed, anechoic wind tunnels with open test sections, high pressure wind tunnels covering up to Mach 21, and dedicated jet testing tunnels. In addition, ONERA has a resident science department that provides engineering services such as model fabrication and instrumentation development, and offers computational fluid dynamics (CFD)/ computer-aided engineering (CAE).
Even now that advanced simulation technologies are available, wind tunnels remain essential destinations on an aircraft’s journey to flight certification. By making early trials of aircraft component designs, designers can find and resolve problems before they endanger human lives, and before too much investment has accumulated.
Acoustics in the ascendancy
Today, commercial plane makers compete to reduce fuel burn and emissions like NOx and noise, meaning ONERA’s focus is broadening. International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) noise regulations place limits on aircraft noise and impose costs when airlines break them, while international government programmes encourage manufacturers to reduce noise during aircraft development. Consequently, the noise that an aircraft makes is being addressed more intensively and earlier in development. As Fabien Mery, ONERA’s wind tunnel R&D team head says, “In the past, wind tunnel testing was more for predicting plane behaviour, but now we see fewer models looking like a plane. We are working more on specific parts of the plane like the engine and air intake, because we need to be more precise, and focus on noise.”
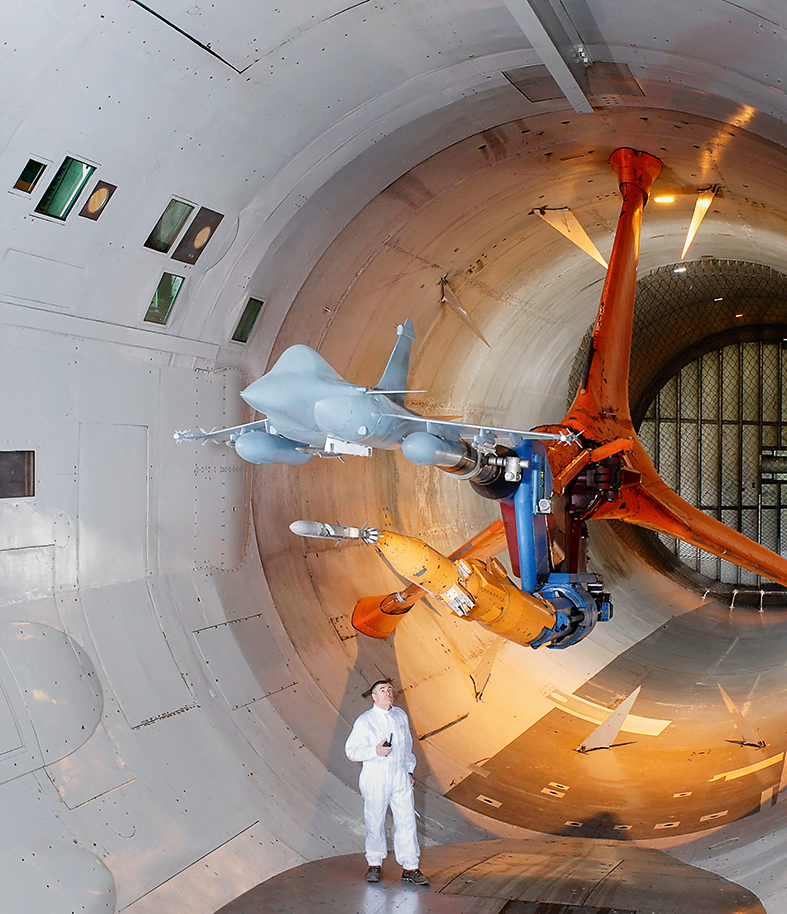
Since 2010, reducing engine noise has been in sharp focus at ONERA’s Modane facility, where they have been working with Safran aircraft engines to research the viability of the manufacturer’s open-rotor jet engine designs. These tests use a 1/5 scale model of the engine, which was made by ONERA’s in-house engineering unit. Using compressed air to spin the engine, the model allows the team to trial different blade geometries, in order to find the optimal balance between thrust, fuel burn, and aeroacoustic noise.
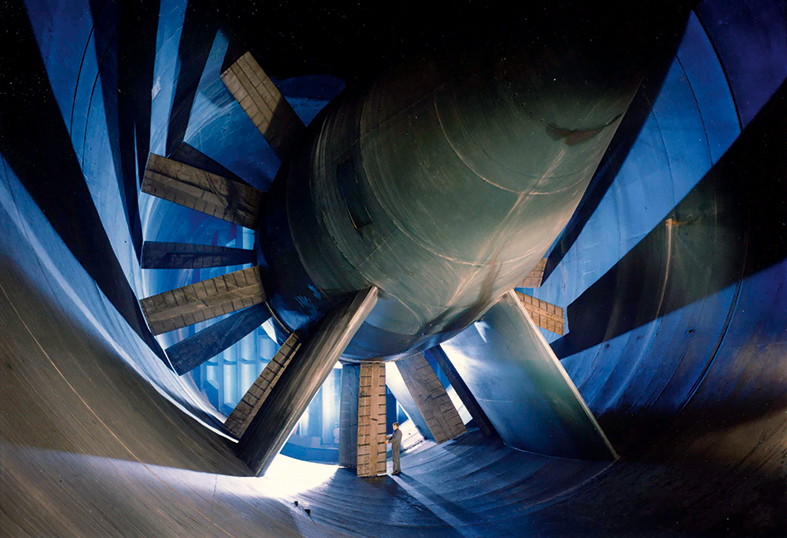 The air in the tunnel is propelled by two large fans connected to a Pelton turbine driven by water extracted from a reservoir above the tunnel
The air in the tunnel is propelled by two large fans connected to a Pelton turbine driven by water extracted from a reservoir above the tunnelSonic testing near Mach 1
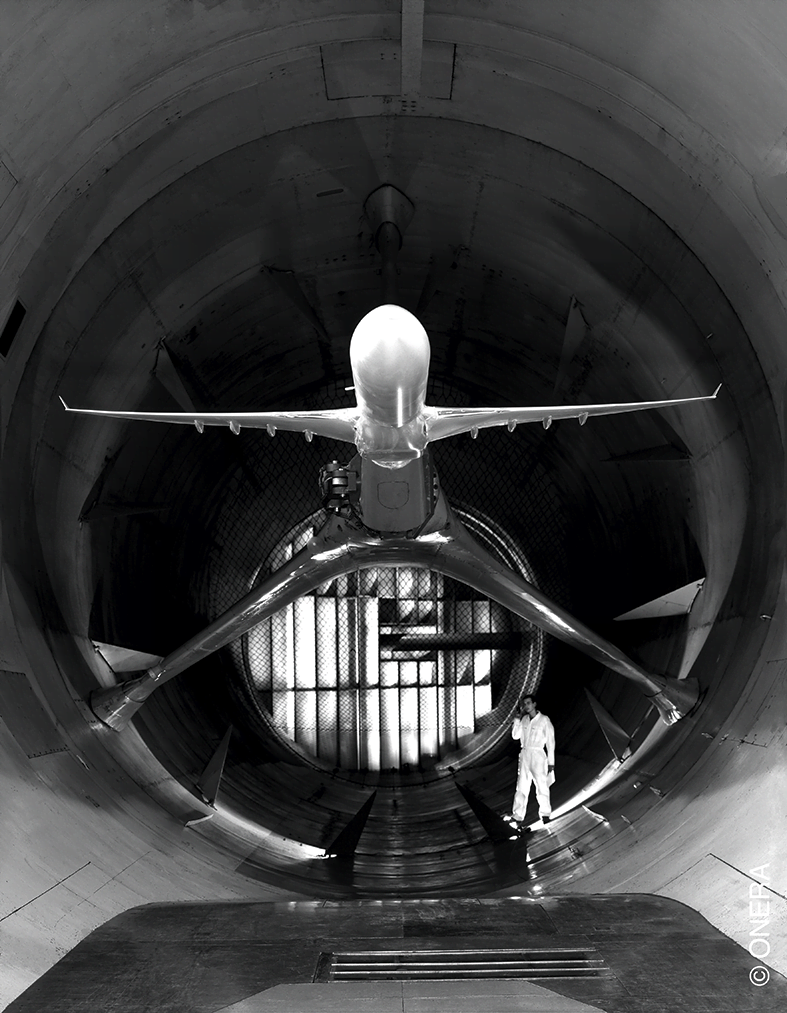
ONERA’s cavernous S1MA wind tunnel at Modane is ideal for this. “Modane is unique in allowing large models that produce the physics we want to observe, in large enough clarity that it is useful,” says Fabien. By allowing testing at up to Mach 1, the S1MA tunnel is also unique in enabling testers to capture data for normal aircraft speeds, which are the most critical for passenger noise exposure due to the time spent at cruise.
For many aeroacoustic noise measurements, a complete anechoic test section – or ‘cart’ – is inserted to give more isolated acoustic conditions. As Fabien says, “Here in Modane, we have a closed test section, and even if it’s not completely anechoic, the liner makes it satisfactory for most measurements.” With bespoke arrays of microphones mounted in the test cart, ONERA’s measurements seek to understand the power, frequency content, and directionality of aeroacoustic noise from models of aircraft components.
Scaling the air
Like the open rotor engine model, scale models of aircraft components or sections are usually around 1/5 the size of the real thing. However, even with a relatively large model, acoustic frequencies are much higher than the design will create in the real world. This is because the frequency of the noise created using a scale model is inversely proportional to the size of the model.
After measurements have been successfully recorded, the high acoustic frequencies must be scaled down. To do this accurately requires ‘dense’ data that has been gathered at a fast sampling rate, so ONERA and Brüel & Kjær collaborated closely on the development of a module for the LAN-XI data acquisition hardware system that samples the signals over 250,000 times per second across many channels. “Brüel & Kjær designed the module to our requirements,” says Fabien. “As a result, ONERA had the first really big system with 100 kHz data acquisition in the world.”
Flexible data acquisition demands
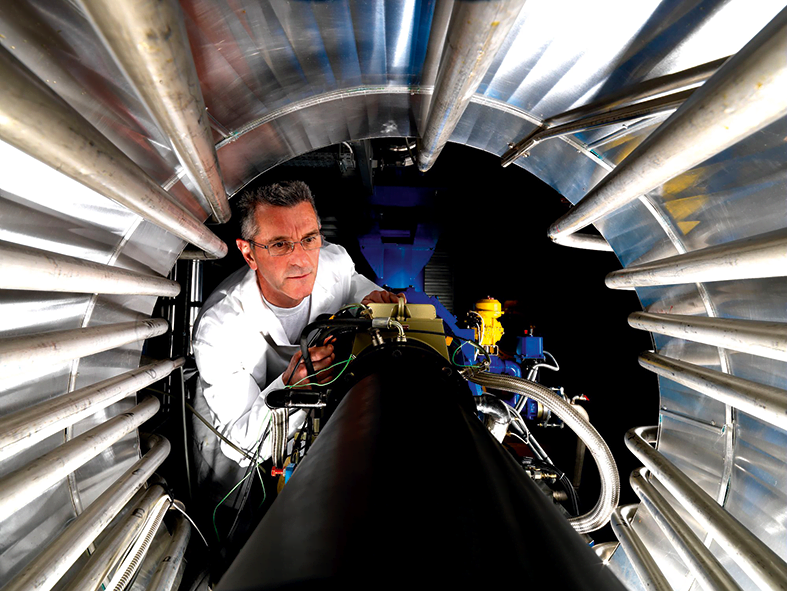
When measuring in the wind tunnel, one challenge for ONERA is avoiding noise in the signals. This is because the analogue cables connecting the transducers to the digital data acquisition system are more affected by electrical noise when measuring high frequencies. The answer is to locate the data acquisition units nearby. “The modular LAN-XI data acquisition system lets us move a module close to each array of transducers, and convert the data to digital ASAP,” says Fabien.
ONERA’s test set-ups change regularly, with microphone arrays at different parts of the wind tunnel for an open rotor engine test than for a new helicopter blade design test. “We split the system all around the circumference of the wind tunnel and then connect the modules with an Ethernet cable,” says Fabien. ONERA also moves data acquisition units around between their different facilities in France, to meet the demands of specific tests. “We have 200 channels in Modane, and more at Saclay and Chatillon, so we can easily combine them to about 500 channels,” he says.
Pivoting on precision
The team needs such high channel counts to gather as much and as accurate data as possible in one go. As Fabien says, “It’s very expensive to make tests, and we do a lot of acoustic beamforming. The classical beamforming antenna uses about 60 microphones, and we use several. So we would even like to get another 100 channels.” Maximizing the meaningful data from each measurement is also critical in a programme of tests, because big decisions hinge on each one. As Fabien says, “Customers are waiting. They need to adapt the test campaign based on the results from one run. We cannot say that we need to put that run in the bin because the gain was not right. So we need to be sure that our measurements are always good.”
Getting the correct range in a wind tunnel is both critical and challenging because ONERA measures very small amplitudes at high frequencies, and low frequencies at very high amplitudes. Their next challenge is testing ultra-high bypass ratio (UBHR) engine designs, which are quieter than open rotor designs, making the important signals harder to discern from the background noise from the wind tunnel’s 8-metre fans. “We need to have something with impressive dynamics,” says Fabien. “The main advantage of our aeroacoustic system is the Dyn-X technology in LAN-XI, with its twin analog-digital convertors and automatic input ranging. It ensures we always get it right the first time.”
Integrated future services
In the near future, ONERA plans to broaden Modane’s capabilities as a one-stop-shop for aircraft testing. “New aircraft designs have always had two separate test campaigns for aerodynamics and aeroacoustics, but we are looking to align them,” says Fabien. The idea is to reduce customer time and expense, and increase data validity by making aerodynamic and aeroacoustic measurements in similar conditions. “We are working on new methods to enable us to perform all the necessary acoustic measurements in non-anechoic environments, where we can de-noise the results.”
The pièce de résistance for ONERA’s vision is that it will enable customers to use their (larger) budget for aerodynamics on aeroacoustics. “We have been doing aerodynamics for 100 years,” says Fabien. “Aeroacoustics is a newer science with fewer established methods and a smaller knowledge base. It is challenging, as they are more dynamic tests. But we need to develop them. We need to understand what’s happening so we can make the best measurements.”
Photos courtesy of ONERA
Clean sky programme – Open rotor engines
This European development programme intends to reduce emissions and lower fuel burn in future aircraft. One of the leading technology contenders is the open rotor engine in development by Snecma. This offers better fuel efficiency and lower emissions, but tends to be noisier due to the lack of shielding when compared to conventional jet engine designs. Aircraft that use the open rotor engine would have to use sound insulation to keep cabin noise down, adding weight. So the research has focused on perfecting the design so it can deliver efficiency savings in use – with minimal extra weight.
Scale models of everything
When measuring smaller aircraft models in wind tunnels, the air needs to be scaled too, to prevent it being too ‘thin’. These are known as Reynolds effects, which ONERA’s testers compensate for when testing. Acoustic frequencies are also scaled, so what would be 50 Hz in the real-world could equate to 250 Hz in the wind tunnel.

Abonnieren Sie unseren Newsletter zum Thema Schall und Schwingung





